When writing an introduction, you should typically use a ‘general to specific’ structure. That is, introduce the particular problem or topic the essay will address in a general sense to provide context, before narrowing down to your particular position and line of argument. Key elements of an introduction Jan 16, · You’re writing an introduction to your essay for two reasons. First, its purpose is to hook your readers so that they will read on and see what you have to say. Second, it will provide a guideline for your topic and main argument, known as the thesis blogger.comted Reading Time: 8 mins Jul 16, · Introduction Definition In a nutshell, the introduction paragraph of an essay is the first paragraph of the paper. Therefore, it is also the first thing your reader will see in your essay. What is the purpose of an introduction paragraph?
Essay Structure |
Writing an academic essay means fashioning a coherent set of ideas into an argument. Because essays are essentially linear—they offer one idea at a time—they must present their essay structure introduction in the order that makes most sense to a reader.
Successfully structuring an essay means attending to a reader's logic, essay structure introduction. The focus of such an essay predicts its structure. It dictates the information readers need to know and the order in which they need to receive it. Thus your essay's structure is necessarily unique to the main claim you're making. Although there are guidelines for constructing certain classic essay types e, essay structure introduction.
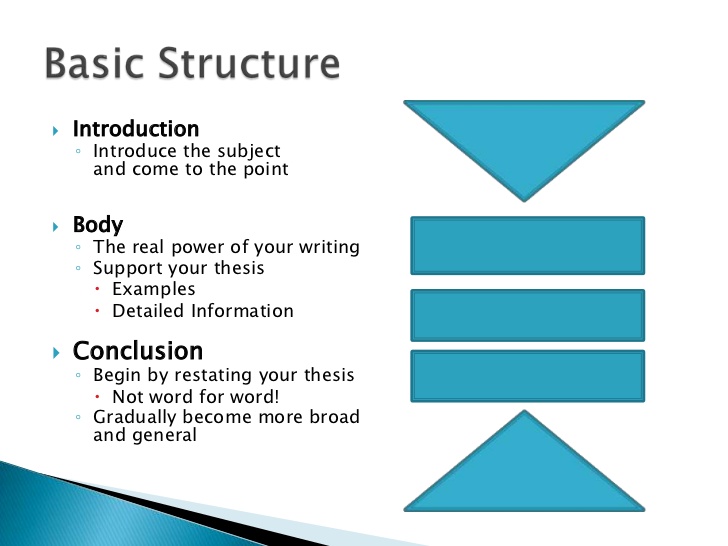
Answering Questions: The Parts of an Essay. A typical essay contains many different kinds of information, often located in specialized parts or sections, essay structure introduction. Even short essays perform several different operations: introducing the argument, analyzing data, raising counterarguments, concluding, essay structure introduction.
Introductions and conclusions have fixed places, but other parts don't. Counterargument, for example, may appear within a paragraph, as a essay structure introduction section, essay structure introduction, as part of the beginning, or before the ending. Background material historical context or biographical information, essay structure introduction, a summary of relevant theory or criticism, the definition of a key term often appears at the beginning of the essay, between the introduction and the first analytical section, but might also appear near the beginning of the specific essay structure introduction to which it's relevant.
It's helpful to think of the different essay sections as answering a series of questions your reader might ask when encountering your thesis. Readers should have questions. If they don't, your thesis is most likely simply an observation of fact, not an arguable claim. To answer the question you must examine your evidence, thus demonstrating the truth of your claim. This "what" or "demonstration" section comes early in the essay, often directly after essay structure introduction introduction.
Since you're essentially reporting what you've observed, this is the part you might have most to say about when you first start writing. But be forewarned: it shouldn't take up much more than a third often much less of your finished essay. If it does, the essay will lack balance and may read as mere summary or description. The corresponding question is "how": How does the thesis stand up to the challenge of a counterargument?
How does the introduction of new material—a new way of looking at the evidence, another set of sources—affect the claims you're making? Typically, an essay will include at least one "how" section. Call it "complication" since you're responding to a reader's complicating questions. This section usually comes after the "what," but keep in mind that an essay may complicate its argument several times depending on its length, and that counterargument alone may appear just about anywhere in an essay.
This question addresses the larger implications of your thesis. It allows your readers to understand your essay within a larger context. In answering "why", your essay explains its own significance. Although you might gesture at this question in your introduction, the fullest answer to it properly belongs at your essay's end.
If you leave it out, your readers will experience your essay as unfinished—or, worse, as pointless or insular.
Mapping an Essay. Structuring your essay according to a reader's logic means examining your thesis and anticipating what a reader needs to know, and in what sequence, in order to grasp and be convinced by your argument as it unfolds. The easiest way to do this is to map the essay's ideas via a written narrative. Such an account will give you a preliminary record of your ideas, and will allow you to remind yourself at every turn of the reader's needs in understanding essay structure introduction idea.
Essay maps ask you to predict where your reader will expect background information, counterargument, close analysis of a primary source, or a turn to secondary source material. Essay maps are not concerned with paragraphs so much as with sections of an essay. They anticipate the major argumentative moves you expect your essay to make. Try making your map like this:. Your map should naturally take you through some preliminary answers to the basic questions essay structure introduction what, how, and why.
It is not a contract, essay structure introduction, though—the order in which the ideas appear is not a rigid one. Essay maps are flexible; they evolve with your ideas. Signs of Trouble. A common structural flaw in college essays is the "walk-through" also labeled "summary" or "description".
Walk-through essays follow the structure of their sources rather than establishing their own. Such essays generally have a descriptive thesis rather than an argumentative one. Be wary of paragraph openers that lead off with "time" words "first," "next," "after," "then" or "listing" words "also," "another," "in addition". Essay structure introduction they essay structure introduction always signal trouble, these paragraph openers often indicate that an essay's thesis and structure need work: they suggest that the essay essay structure introduction reproduces the chronology of the source text in the case of time words: first this happens, then that, and afterwards another thing.
or simply lists example after example "In addition, essay structure introduction, the use of color indicates another way that the painting differentiates between good and evil", essay structure introduction. CopyrightElizabeth Abrams, for the Writing Center at Harvard University.
Skip to main content. Main Menu Utility Menu Search. Harvard College Writing Program HARVARD. Home FAQ Schedule an appointment Writing Resources Writing Resources Writing Advice: The Barker Underground Blog Contact Us. Answering Questions: The Parts of an Essay A typical essay contains many different kinds of information, often located in specialized parts or sections, essay structure introduction.
Mapping an Essay Structuring your essay according to a reader's logic means examining your thesis and anticipating what a reader needs to know, and in what sequence, essay structure introduction, in order to grasp and be convinced by your argument as it unfolds. Try making your essay structure introduction like this: State your thesis in a sentence or two, then write another sentence saying why it's important to make that claim. Indicate, in other words, what a reader might learn by exploring the claim with you.
Here you're anticipating your answer to the "why" question that you'll eventually flesh out in your conclusion. Begin your next sentence like this: "To be convinced by my claim, the first thing a reader needs to know is. This will start you off on answering the "what" question. Alternately, you may find that the first thing your reader needs to know is some background information.
Begin each of the following sentences like this: "The next thing my reader needs to know is. Continue until you've mapped out your essay. Signs of Trouble A common structural flaw in college essays is the "walk-through" also labeled "summary" or "description". Writing Resources Strategies for Essay Writing How to Read an Assignment Moving from Essay structure introduction to Topic How to Do a Close Reading Overview of the Academic Essay Essay Structure Developing A Thesis Beginning the Academic Essay Outlining Counterargument Summary Topic Sentences and Signposting Transitioning: Beware of Velcro How to Write a Comparative Analysis Ending the Essay: Conclusions Revising the Draft Editing the Essay, Part One Editing the Essay, Part Two Tips on Grammar, Punctuation and Style Brief Guides to Writing in the Disciplines.
Quick Links Schedule an Appointment Writing Resources Harvard Guide to Using Sources HarvardWrites Employment Follow HCWritingCenter. Copyright © The President and Fellows of Harvard College Accessibility Digital Accessibility Report Copyright Infringement.
Learn to Write an Introduction Paragraph!
, time: 2:02How to Write an Essay Introduction | Tips + Examples | HandMadeWriting

Feb 04, · A good introduction paragraph is an essential part of any academic essay. It sets up your argument and tells the reader what to expect. The main goals of an introduction are to: Catch your reader’s attention. Give background on your topic. Present your thesis —the central point of your essay Jan 16, · You’re writing an introduction to your essay for two reasons. First, its purpose is to hook your readers so that they will read on and see what you have to say. Second, it will provide a guideline for your topic and main argument, known as the thesis blogger.comted Reading Time: 8 mins Jul 16, · Introduction Definition In a nutshell, the introduction paragraph of an essay is the first paragraph of the paper. Therefore, it is also the first thing your reader will see in your essay. What is the purpose of an introduction paragraph?
No comments:
Post a Comment